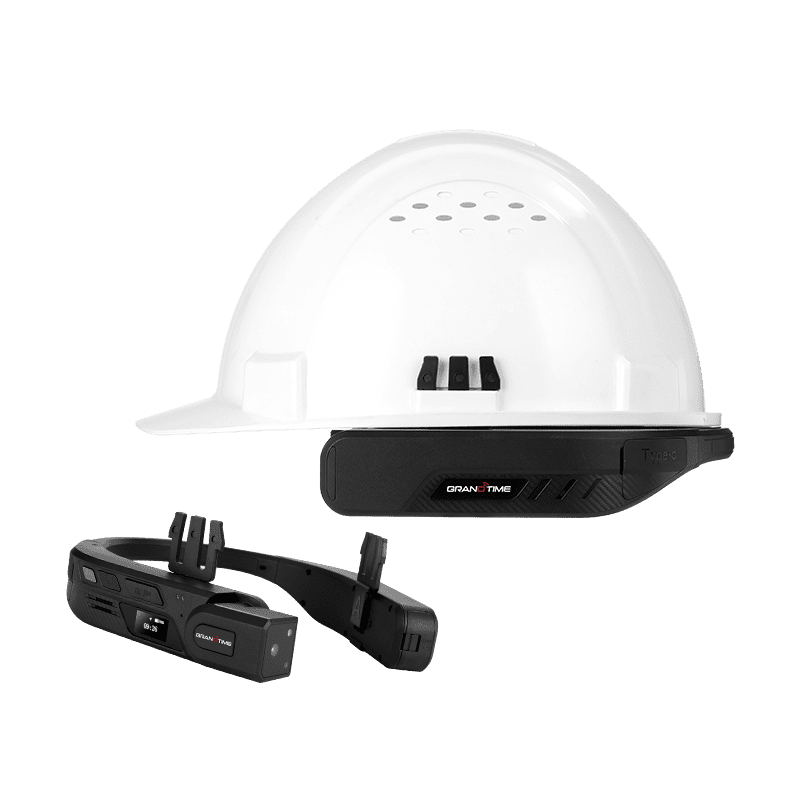
In 2026, AI-powered smart glasses are evolving from experimental prototypes to critical tactical equipment for law enforcement and public security agencies worldwide. These devices provide "superhuman" capabilities by merging real-time data with an officer's direct field of view.
1. Advanced Tactical Capabilities
AI glasses enhance field operations by providing hands-free access to critical intelligence:
Facial & Plate Recognition: Current systems (like those deployed in China and Dubai) can identify suspects and vehicle license plates within 1–2 seconds from up to 30 meters away.
"Friend or Foe" Identification: Future AR overlays will visually distinguish team members and on-duty officers from suspects at a distance, significantly reducing the risk of friendly fire in high-stress scenarios.
Enhanced Sensory Perception: Next-gen optics allow officers to "see through" smoke or darkness using thermal and low-light sensors, and even peek around corners by linking with weapon-mounted cameras.

2. Proactive Public Security & Prevention
Beyond identification, AI enables proactive threat assessment:
Crowd & Movement Analytics: Glasses can estimate crowd density and identify unusual movement patterns that may indicate a developing incident.
Predictive Policing: By connecting to centralized databases, AI glasses can suggest high-risk areas for patrolling based on real-time crime data and historical patterns.
Threat Detection: AI algorithms are now capable of identifying firearms and suspicious objects in crowded environments like airports or malls.
3. Investigation & Field Efficiency
Digital Crime Scene Preservation: Augmented reality apps allow the first officer on a scene to place virtual markers and capture a 3D digital twin of the evidence without disturbing the physical site.
Real-time Transcription & Translation: Field units use AI for instant translation of foreign languages and automated generation of incident reports from audio feeds, freeing up hours of administrative time.
4. Critical Challenges & Ethical Concerns
The adoption of this technology in 2026 faces significant scrutiny:
Privacy & Mass Surveillance: Continuous recording in public spaces raises profound legal questions about bystander consent and has triggered probes by the EU's Data Privacy Commissioner under the EU AI Act.
Accuracy & Bias: Historical tests have shown high rates of "wrongful identification" in certain demographics, leading to calls for human-in-the-loop verification before any arrests are made.
Accessibility for Non-State Actors: The "collapse of the barrier to entry" means high-end facial recognition is now available to the general public through consumer-grade smart glasses, posing new risks for witnesses and high-profile individuals.